
What Is REST API and How It Works
In modern web and mobile application development, APIs play a critical role in enabling
communication between different systems. One of the most widely used API architectures today
is the REST API. Understanding what a REST API is and how it works is essential for developers,
testers, and anyone working with software systems.
This guide explains REST APIs in a clear and beginner-friendly way, covering core concepts,
principles, request–response flow, and real-world use cases.
What Is an API?
API stands for Application Programming Interface.
An API allows two software applications to communicate with each other.
It defines a set of rules and formats that applications follow to request and exchange data.
For example, when a mobile app fetches data from a server or a website displays user information
from a database, an API is usually responsible for handling that communication.
What Is a REST API?
REST stands for Representational State Transfer.
A REST API is an API that follows REST architectural principles to enable communication
between a client and a server over the internet.
REST APIs use standard HTTP protocols and are designed to be lightweight, scalable,
and easy to understand. They are commonly used in web applications, mobile apps,
microservices, and cloud-based systems.
Key Principles of REST Architecture
REST is not a protocol but an architectural style.
A RESTful API follows a set of constraints that make it reliable and scalable.
1. Client-Server Separation
REST APIs separate the client and server.
The client handles the user interface, while the server manages data and business logic.
This separation allows both sides to evolve independently.
2. Stateless Communication
REST APIs are stateless, meaning each request from the client contains all the information
the server needs to process it.
The server does not store client session data between requests.
Statelessness improves scalability and reliability,
as each request is independent of previous requests.
3. Resource-Based Design
In REST, everything is treated as a resource.
A resource can be a user, product, order, or any data entity.
Each resource is identified by a unique URL.
For example:
/users – represents all users
/users/1 – represents a specific user
4. Use of Standard HTTP Methods
REST APIs use standard HTTP methods to perform operations on resources.
Each method has a specific purpose.
- GET – Retrieve data
- POST – Create new data
- PUT – Update existing data
- PATCH – Partially update data
- DELETE – Remove data
5. Uniform Interface
REST APIs follow a consistent and predictable structure.
This uniformity makes APIs easier to understand and use,
even for developers who are new to the system.
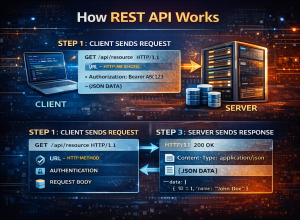
How REST API Works
A REST API works using a request–response model.
The client sends an HTTP request to the server,
and the server processes the request and returns an HTTP response.
Step 1: Client Sends a Request
The client sends a request to a specific API endpoint.
The request includes:
- URL (endpoint)
- HTTP method (GET, POST, etc.)
- Headers (authentication, content type)
- Optional request body (for POST or PUT)
Step 2: Server Processes the Request
The server receives the request, validates it,
checks permissions, processes business logic,
and interacts with the database if required.
Step 3: Server Sends a Response
After processing the request, the server sends a response back to the client.
The response usually contains:
- HTTP status code
- Response headers
- Response body (often in JSON format)
Common HTTP Status Codes in REST APIs
HTTP status codes indicate the result of an API request.
They help clients understand whether a request succeeded or failed.
- 200 OK – Request successful
- 201 Created – Resource created successfully
- 400 Bad Request – Invalid request data
- 401 Unauthorized – Authentication required
- 403 Forbidden – Access denied
- 404 Not Found – Resource not found
- 500 Internal Server Error – Server-side error
Why REST APIs Are So Popular
REST APIs are widely adopted because they are simple, flexible, and scalable.
They work over standard HTTP, which makes them compatible with almost any platform or language.
Developers prefer REST APIs because they are easy to test,
easy to document, and easy to integrate with frontend applications.
REST API vs SOAP API
REST APIs are often compared with SOAP APIs.
SOAP is a protocol with strict standards,
while REST is an architectural style with flexibility.
REST APIs are lightweight and usually use JSON,
whereas SOAP APIs rely on XML and are more complex.
This is why REST is more commonly used in modern applications.
Real-World Use Cases of REST APIs
REST APIs are used in almost every modern application.
Some common use cases include:
- Web and mobile applications
- Authentication and authorization systems
- Payment gateways
- Cloud services and microservices
- Third-party integrations
Best Practices for Designing REST APIs
A well-designed REST API improves performance and developer experience.
Some best practices include:
- Use meaningful and consistent endpoint names
- Follow proper HTTP methods
- Return clear and correct status codes
- Use JSON as the response format
- Implement authentication and authorization
Conclusion
REST APIs are the backbone of modern application development.
They provide a simple and scalable way for systems to communicate over the internet.
By understanding what a REST API is and how it works,
developers can build better, more maintainable applications.
Mastering REST API concepts is essential for backend development,
frontend integration, and system design.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer,
REST APIs remain a fundamental skill in today’s technology landscape.

